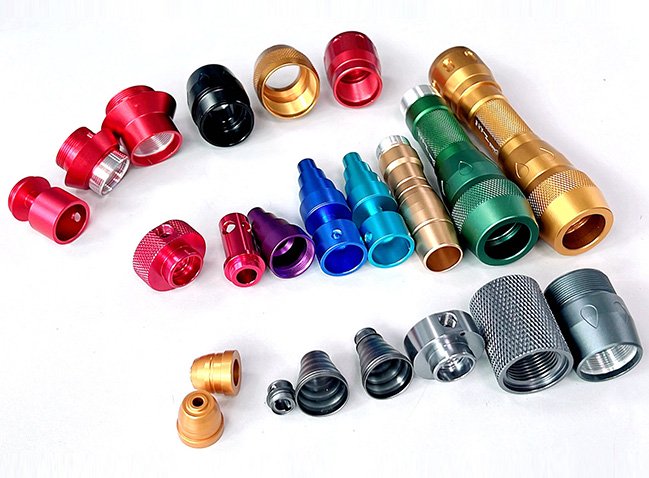
Precision CNC Machining: Advanced Turning & Milling Solutions for High-Quality Parts
Precision CNC machining has become a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, enabling the production of highly accurate and complex components across industries such as aerospace, medical devices, electronics, and industrial equipment. Leveraging advanced CNC turning and milling systems, manufacturers can deliver custom parts with exceptional dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and repeatability.
Core Advantages of Precision CNC Machining
Exceptional Dimensional Accuracy
High-precision CNC systems combined with stable machining environments ensure extremely tight tolerances, making it suitable for high-end applications where precision is critical.
Superior Surface Quality
Smooth tool movement and precise cutting parameter control result in excellent surface finishes, reducing post-processing needs and improving part performance.
Complex Geometries Made Easy
Multi-axis machining and advanced tool path planning allow for the creation of complex shapes that are difficult or impossible with traditional machines.
Consistent Stability and Repeatability
Once a program is established, identical high-precision parts can be produced in batches, minimizing variability caused by manual intervention.
Wide Range of Material Compatibility
From stainless steel and titanium to aluminum alloys and engineering plastics, precision CNC machining can handle diverse materials by selecting appropriate tools and processes.
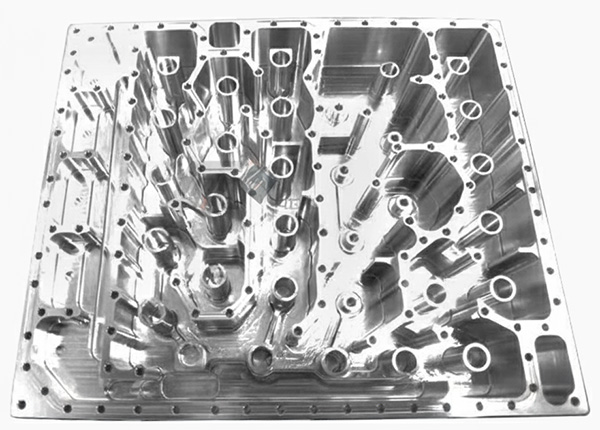
Key Process Considerations
Machine Accuracy
Precision machining requires high-rigidity, stable CNC machines that are regularly calibrated to maintain accuracy.
Tool Selection
High-performance tools, such as carbide and diamond-coated options, are essential for achieving precise cutting across different materials.
Cutting Parameter Control
Feed rate, spindle speed, and cutting depth must be carefully configured according to material properties and tool conditions to achieve optimal results.
Fixtures and Workpiece Clamping
High-precision fixtures minimize workpiece displacement and deformation, forming the foundation of dimensional accuracy.
Temperature and Environmental Control
Material expansion due to temperature fluctuations can impact tolerances. Precision CNC machining is often conducted in temperature-controlled workshops to maintain consistency.
Differences Between Standard and Precision CNC Machining
- Tolerance Requirements: Standard machining tolerances may be around 0.05mm, whereas precision CNC machining can achieve 0.005mm or lower.
- Machining Speed and Process Planning: Precision machining favors slow, stable cutting for quality; standard machining emphasizes efficiency.
- Inspection Standards: Precision machining uses high-precision measurement tools like CMMs and laser measurement systems throughout the production process.
- Equipment Investment: Precision CNC machines are more expensive and often feature temperature control, automatic lubrication, and monitoring systems.
Typical Applications of Precision CNC Machining
- Aerospace: Turbine blades, airframe components, and other high-precision parts rely on CNC machining for both accuracy and strength.
- Medical Devices: Artificial joints, dental implants, and surgical instruments demand tight tolerances, biocompatibility, and superior surface finish.
- Precision Mold Manufacturing: CNC machining ensures long mold life and high forming accuracy.
- Optical Instruments: Components like optical barrels, precision turntables, and mounts require extreme dimensional and geometric accuracy.
- Electronics and Communication Equipment: Housings, connectors, and heat-dissipation parts depend on high-precision CNC machining for both functionality and aesthetics.
CNC Precision Machining Process Overview
- Drawing and Process Analysis: Engineers review part drawings to determine machining sequence, tool selection, and cutting parameters.
- Programming: CAM software generates tool paths, which are then input and tested in the CNC system.
- Trial Cutting and Adjustments: Initial trial runs verify dimensions, surface finish, and allow for parameter tuning.
- Batch Production: Approved samples move to full-scale production with automated inspections and tool changes.
- Quality Inspection and Delivery: High-precision measurement systems ensure every part meets customer specifications before shipment.
Key Factors Affecting CNC Machining Quality
- Tool wear and replacement schedules
- Machine stability and routine maintenance
- Material consistency and batch quality
- Program optimization and tool path planning
- Environmental control and thermal compensation
Conclusion
Precision CNC machining is more than just a manufacturing technique—it is a critical driver of industrial competitiveness. From high-end machinery and medical devices to aerospace and consumer electronics, its impact is widespread. With continuous improvements in CNC technology and process expertise, the future of precision CNC machining promises smarter, faster, and more reliable production, delivering high-quality components across industries.



